Perpendicular and angle bisectors
What is an angle bisector?
In this lesson we’ll look at how to use the properties of perpendicular and angle bisectors to find out more information about geometric figures.
Hi! I'm krista.
I create online courses to help you rock your math class. Read more.
Angle bisectors
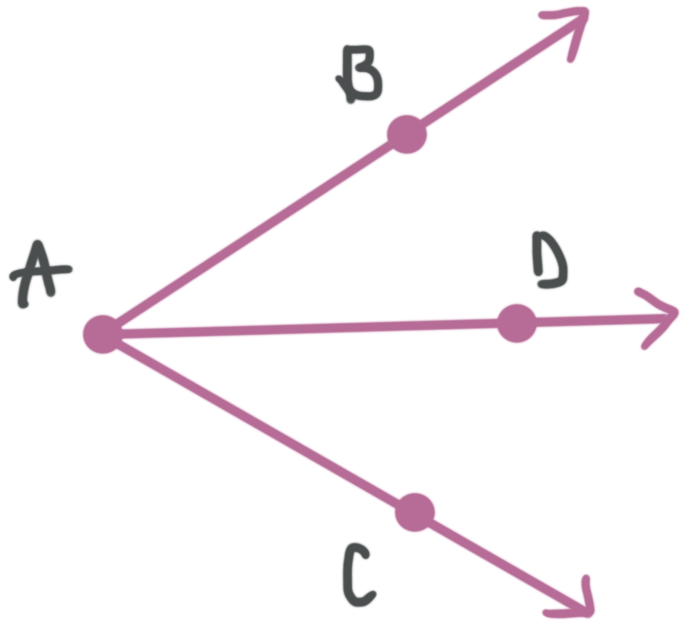
An angle bisector goes through the vertex of an angle and divides the angle into two congruent angles that each measure half of the original angle. If ???\vec{AD}??? bisects ???\angle CAB???,
then
???m\angle DAB=m\angle CAD???
???m\angle DAB=\frac12m\angle CAB=m\angle CAD???
???2m\angle DAB=m\angle CAB=2m\angle CAD???
How to solve problems with perpendicular bisectors and angle bisectors
Take the course
Want to learn more about Geometry? I have a step-by-step course for that. :)
Solving for values in a polygon using perpendicular or angle bisectors
Example
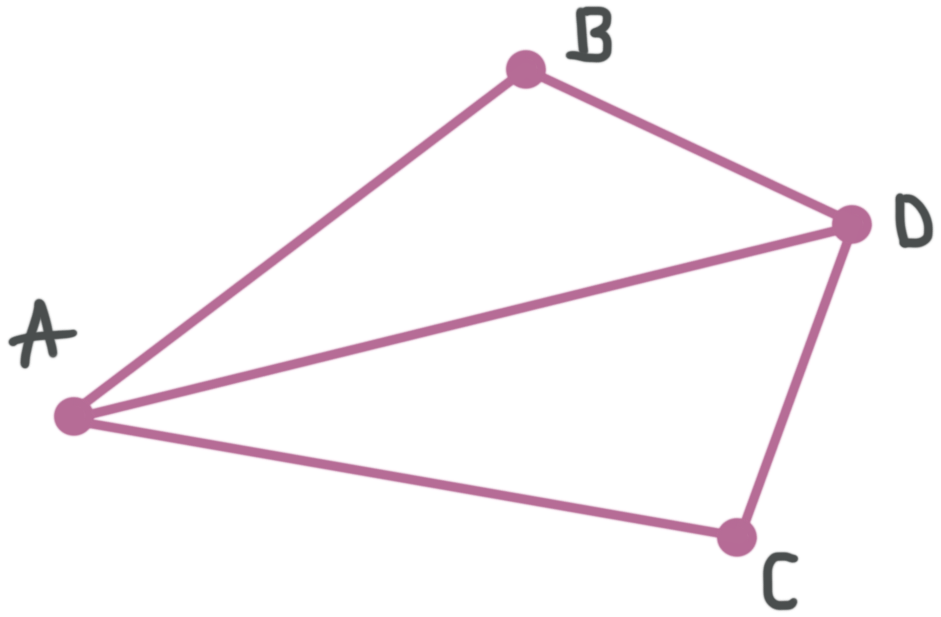
If ???m\angle BAD=31^\circ??? and ???m\angle BDC=66^\circ???, and ???\overline{AD}??? is a bisector of both ???\angle BAC??? and ???\angle BDC???, what is ???m\angle C????
Using what we already know, we can say
???m\angle BAD=m\angle DAC=31^\circ???
and
???m\angle ADC=\frac{1}{2}m\angle BDC=\frac{1}{2}\cdot 66^\circ =33^\circ???
The three angles of any triangle add up to ???180^\circ??? and we have ???\triangle ACD???, so
???31^\circ +33^\circ +m\angle C=180^\circ???
???64^\circ +m\angle C=180^\circ???
???m\angle C=116^\circ???
An angle bisector goes through the vertex of an angle and divides the angle into two congruent angles that each measure half of the original angle.
Perpendicular bisectors
A perpendicular bisector crosses a line segment at its midpoint and forms a right angle where it crosses. ???\overline{CD}??? is a perpendicular bisector of ???\overline{AB}??? at point ???E???.
This tells us that
???m\angle AEC=m\angle CEB=m\angle AED=m\angle BED=90^\circ???
???\overline{AE}=\overline{EB}???
Let’s look at a few more example problems.
Example
Find the value of ???y??? if ???\overline{CM}??? is a perpendicular bisector of ???\overline{AJ}???.
Because ???\overline{CM}??? is a perpendicular bisector of ???\overline{AJ}???, we know that ???\overline{AM}=\overline{MJ}???, so we can say
???5y+8=8.2y???
???8=3.2y???
???y=2.5???
Let’s look at one more problem.
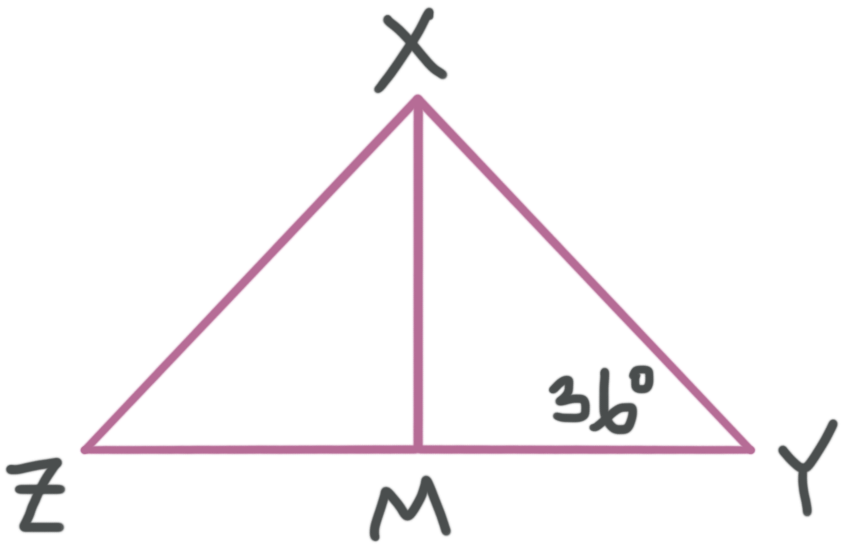
Example
Find ???m\angle YXM??? if ???\overline{XM}??? is a perpendicular bisector of ???\overline{ZY}???.
We know ???\angle XMY??? is a right angle, so ???m\angle XMY=90^\circ???. The three angles of any triangle add up to ???180^\circ??? and we have ???\triangle XMY???.
???90^\circ +36^\circ +m\angle YXM=180^\circ???
???126^\circ +m\angle YXM=180^\circ???
???m\angle YXM=54^\circ???